# 异常机制
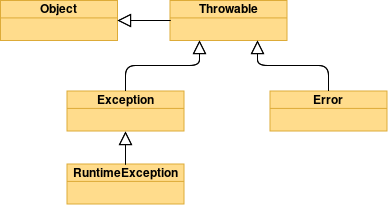
Throwable 类是所有异常或错误的超类,它有两个子类:Error 和 Exception,分别表示错误和异常
错误和异常(Error / Exception)
- Error:由 JVM 所侦测到的无法预期的错误,由于这是属于 JVM 层次的严重错误,导致 JVM 无法继续执行,如 OutOfMemoryError,程序本身往往无法处理,因此无需捕获,也不能捕获
- Exception:主要是由于程序设计的瑕疵或外界的输入而引起的问题,可以由程序捕获和恢复
可查异常和不可查异常(Checked / Unchecked Exception)
- 可查异常:checked at compile time,属于可以预料的异常,编译器会检查代码,要求你必须对这些异常进行处理,即 try-catch 捕获或 throws 向上抛出,如:IOException,FileNotFoundException
- 不可查异常:not checked at compile time,checked at runtime,编译器不要求强制处置的异常,无法提前预期的异常,主要包括 RuntimeException 和 Error
运行时异常和非运行时异常(Runtime / Non-Runtime)
- 运行时异常:指 RuntimeException 及其子类,这些异常是不检查异常,程序不强制要求捕获,也没有必要进行捕获处理,一般交由 JVM 进行处理
- NullPointerException,IndexOutOfBoundsException,ClassCastException,ArithmeticException
- 非运行时异常:除了运行时异常以外的异常,包括用户自定义异常,强制要求进行处理
# try-catch-finally
程序运行过程中可能出现异常,异常将导致程序提前中断,为了保证程序在出现异常时,仍然可以正常执行,需要设置异常处理
try: 放置可能出现异常的代码catch: 从上到下依次匹配 catch 块,一旦发现匹配 catch 块,忽略后续其他 catch- 因此范围小的异常应该放在范围大的后面(否则编译报错)
finally: 最后执行且总是执行,常用于资源回收,中断数据库连接,文件关闭等操作- 若出现异常,且
catch匹配失败,则 finally 执行完毕后,使用 JVM 默认异常处理(抛出异常) - finally 总是在控制转移语句(break,continue,return 等)执行之前执行
- 若出现异常,且
代码样例
try {
} catch (Exception e) {
} catch (IOException e) {
}
// 会报错,因为 IOException 继承 Exception,IOException永远不会被匹配
try {
int res = 5 / 0;
} finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
/* Output
finally
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at driver.Driver.main(Driver.java:7) */
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
执行顺序
- try 语句中出现异常的代码之后的代码不会执行
- finally 中的代码总会被执行,除非之前的代码中出现了
System.exit(0) - try 中含有 return:先执行 return 前的代码,暂时保存 return 信息,再执行 finally,最后返回结果
- catch 中含有 return:先执行 return 前的代码,暂时保存 return 信息,再执行 finally,最后返回结果
- finally 中含有 return:try 中的 return 会失效
代码样例1
try {
int res = 2/0;
System.out.println("try");
} catch(ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println("catch");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
System.out.println("There");
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
catch
finally
There
1
2
3
2
3
代码样例2
try {
int res = 2/0;
System.out.println("try");
} catch(ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println("catch");
System.exit(0);
} finally {
System.out.println("finally"); // 不会执行
}
System.out.println("There");
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
catch
1
代码样例3
// try中带有return时,会先执行return前的代码,然后暂时保存需要return的信息
// 再执行finally中的代码,最后再通过return返回之前保存的信息
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("return: i=" + test());
}
public static int test() {
int i = 0;
try {
System.out.println("try: i=" + i);
return i;
} catch(ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println("catch");
} finally {
i++;
System.out.println("finally: i=" + i);
}
i++;
System.out.println("There: i=" + i);
return i;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
try: i=0
finally: i=1
return: i=0
1
2
3
2
3
代码样例4
public static int test() {
int i = 0;
try {
System.out.println("try: i=" + i);
int res = 5/0;
} catch(ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println("catch: i=" + i);
return i;
} finally {
i++;
System.out.println("finally: i=" + i);
}
i++;
System.out.println("There: i=" + i);
return i;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
try: i=0
catch: i=0
finally: i=1
return: i=0
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
代码样例5
public static int test() {
int i = 0;
try {
System.out.println("try: i=" + i);
return i;
} catch(ArithmeticException ae) {
i++;
System.out.println("catch: i=" + i);
return i;
} finally {
i++;
System.out.println("finally: i=" + i);
return i;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// try 失效
try: i=0
finally: i=1
return: i=1
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
public static int test() {
int i = 0;
try {
System.out.println("try: i=" + i);
int res = 5/0;
return i;
} catch(ArithmeticException ae) {
i++;
System.out.println("catch: i=" + i);
return i;
} finally {
i++;
System.out.println("finally: i=" + i);
return i;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// catch 失效
try: i=0
catch: i=1
finally: i=2
return: i=2
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# throws / throw
1. throws
- 可以通过
throws关键字向方法调用者说明该方法可能抛出的异常 - 调用使用了
throws的方法时,需要对声明的异常进行捕获和处理 - 如果不打算在本层进行异常处理,则调用者也可以使用
throws将异常继续交由上层 - 主方法也可使用
throws,则代表该异常将交给 JVM 进行处理
class Test {
public static int divide(int x, int y) throws Exception {
return x/y;
}
/*
* 1 使用try-catch进行捕获
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Test.divide(10, 2);
} catch(Exception e) {
// Do something
}
}
/*
* 2 或者继续交给上层调用者进行处理
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test.divide(10, 2);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2. throw
异常可以由系统自动实例化对象随后抛出,也可以通过 throw 手工进行异常类的实例化对象抛出
throw 语句执行后,后续语句将不会再执行
class Test {
/*
* 如果不打算使用throws向上抛出由调用者进行异常处理
* 则需要在方法内使用try-catch进行捕获处理
*/
public static int divide(int x, int y) throws Exception {
if (y == 0) {
throw new Exception("y cannot be zero");
System.out.println("Here"); // 该语句不会执行,unreachable
}
return x/y;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 自定义异常
Java 内置了许多异常类型,但是在具体项目中仍然可能不足以满足需求,这时可以自定义异常
两种自定义异常的选择
- 继承
Exception: 强制性处理异常 - 继承
RuntimeException: 选择性异常处理
class MyException extends RuntimeException {
public MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
class Test {
public void foo(int n) throws MyException{
if (n > 0) throw new MyException("Positive");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 断言
使用关键字 assert,对指定内容进行判断,默认情况下,Java 并不开启断言,需要使用参数 -ea 开启
当断言开启时,如果判断结果为 false,则会抛出 AssertionError
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
assert num == 30 : "False! num is not 30"; // Error Message
System.out.println(num);
}
}
java -ea Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9